An ER (Entity-Relationship) diagram is a graphical representation of entities and their relationships to each other in a database. It is a conceptual tool used in database design to describe the data and relationships that are important to an organization. ER diagrams use various symbols and connectors to illustrate entities, attributes, and relationships.
a. List the (nonweak) entity types in the ER diagram.
➲bank, account, loan, customer
b. Is there a weak entity type? If so, give its name, partial key, and identifying the relationship.
c. What constraints do the partial key and the identifying relationship of the weak entity type specified in this diagram?
➲a bank_branch cannot exist without an associated bank
d. List the names of all relationship types, and specify the (min, max) constraint on each participation of an entity type in a relationship type. Justify your choices.
e. List concisely the user requirements that led to this ER schema design.
➲a bank entity that can be related to many bank branches where each branch can have many accounts and loans to customers. each customer can have a number of loans and accounts. each loan and account must be associated with a customer
f. Suppose that every customer must have at least one account but is restricted to at most two loans at a time and that a bank branch cannot have more than 1000 loans. How does this show up on the (min, max) constraints?
Consider the ER diagram shown below for part of a BANK database. Each bank can have multiple branches, and each branch can have multiple accounts and loans.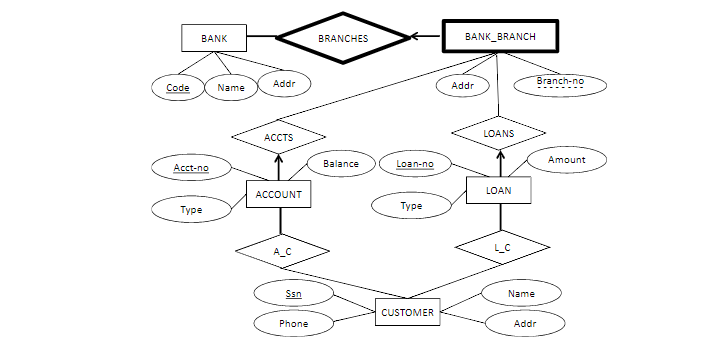 a. List the (nonweak) entity types in the ER diagram.
a. List the (nonweak) entity types in the ER diagram.
➲Customer, Account, Loan, Bank
➲Bank_Branch (Branch - no: string, Code: string, Addr: string)
ER diagram of Bank has the following description :
- Bank
have Customer.
- Banks
are identified by a name, code, address of main office.
- Banks
have branches.
- Branches
are identified by a branch_no., branch_name, address.
- Customers
are identified by name, cust-id, phone number, address.
- Customer
can have one or more accounts.
- Accounts
are identified by account_no., acc_type, balance.
- Customer
can avail loans.
- Loans
are identified by loan_id, loan_type and amount.
- Account
and loans are related to bank’s branch.
ER Diagram of Bank Management System :
This bank ER diagram illustrates key information about bank,
including entities such as branches, customers, accounts, and loans. It allows
us to understand the relationships between entities.
Entities and their Attributes are :
- Bank
Entity: Attributes of Bank Entity are Bank Name, Code, and
Address.
Code is the Primary Key for the Bank Entity. - Customer
Entity: Attributes of Customer Entity are Customer_id, Name,
Phone Number and Address.
Customer_id is Primary Key for Customer Entity. - Branch
Entity: Attributes of Branch Entity are Branch_id, Name and
Address.
Branch_id is Primary Key for Branch Entity. - Account
Entity: Attributes of Account Entity are Account_number,
Account_Type and Balance.
Account_number is Primary Key for Account Entity. - Loan
Entity: Attributes of Loan Entity are Loan_id, Loan_Type and
Amount.
Loan_id is Primary Key for Loan Entity.
Relationships are :
- Bank
has Branches => 1 : N
One Bank can have many Branches but one Branch can not belong to many Banks, so the relationship between Bank and Branch is one to many relationship.
- Branch
maintain Accounts => 1 : N
One Branch can have many Accounts but one Account can not belong to many Branches, so the relationship between Branch and Account is one to many relationship.
- Branch
offer Loans => 1 : N
One Branch can have many Loans but one Loan can not belong to many Branches, so the relationship between Branch and Loan is one to many relationship.
- Account
held by Customers => M : N
One Customer can have more than one Accounts and also One Account can be held by one or more Customers, so the relationship between Account and Customers is many to many relationship.
- Loan
availed by Customer => M : N
(Assume loan can be jointly held by many Customers).
One Customer can have more than one Loans and also One Loan can be availed by one or more Customers, so the relationship between Loan and Customers is many to many relationship.
a. List the (nonweak) entity types in the ER diagram.
➲bank, account, loan, customer
b. Is there a weak entity type? If so, give its name, partial key, and identifying the relationship.
➲weak entity type: bank_branch
➲partial key: branch_no
➲identifying relationship: branches
➲partial key: branch_no
➲identifying relationship: branches
c. What constraints do the partial key and the identifying relationship of the weak entity type specified in this diagram?
➲a bank_branch cannot exist without an associated bank
d. List the names of all relationship types, and specify the (min, max) constraint on each participation of an entity type in a relationship type. Justify your choices.
➲branches- bank:bank_branch, 1:N
➲accts- bank_branch:account, 1:N
➲loans- bank_branch:loan, 1:N
➲a_c- account: customer, N:M
➲l_c- loan:customer, N:M
➲accts- bank_branch:account, 1:N
➲loans- bank_branch:loan, 1:N
➲a_c- account: customer, N:M
➲l_c- loan:customer, N:M
e. List concisely the user requirements that led to this ER schema design.
➲a bank entity that can be related to many bank branches where each branch can have many accounts and loans to customers. each customer can have a number of loans and accounts. each loan and account must be associated with a customer
f. Suppose that every customer must have at least one account but is restricted to at most two loans at a time and that a bank branch cannot have more than 1000 loans. How does this show up on the (min, max) constraints?
➲a_c-customer to accounts: (1,N)
➲l_c-customer to loans: (0,2)
➲loans-bank_branch to loan: (0,1000)
➲l_c-customer to loans: (0,2)
➲loans-bank_branch to loan: (0,1000)
Consider the ER diagram shown below for part of a BANK database. Each bank can have multiple branches, and each branch can have multiple accounts and loans.
 a. List the (nonweak) entity types in the ER diagram.
a. List the (nonweak) entity types in the ER diagram. ➲Customer, Account, Loan, Bank
b. Is there a weak entity type? If so, give its name, partial key, and identifying the relationship
➲Bank_Branch is a weak entity. Its partial key is Branch-no and its identifying relationship is BRANCHES with Bank.
c. What constraints do the partial key and the identifying relationship of the weak entity type specified in this diagram?
➲The constraint of the partial key Branch - no is that we need to combine Branch - no with Code, the key from its owner entity set Bank, to uniquely identify a Bank_Branch.
The constraints of the identifying relationship are:
1) The identifying relationship between the owner entity set, Bank, and the weak entity set, Bank_Branch must be one too many and Bank_Branch could only have one Bank as its owner.
2) The weak entity set, Bank_Branch, must have total participation in the identifying relationship set, BRANCHES.
➲The constraint of the partial key Branch - no is that we need to combine Branch - no with Code, the key from its owner entity set Bank, to uniquely identify a Bank_Branch.
The constraints of the identifying relationship are:
1) The identifying relationship between the owner entity set, Bank, and the weak entity set, Bank_Branch must be one too many and Bank_Branch could only have one Bank as its owner.
2) The weak entity set, Bank_Branch, must have total participation in the identifying relationship set, BRANCHES.
d. Translate this ER model into a relational schema (not SQL notation)
➲Customer (Ssn: string, Phone:string, Name: string, Addr: string)
➲Bank (Code: string, Name: string, Addr: string) ➲Bank_Branch (Branch - no: string, Code: string, Addr: string)
➲Account (Acct - no: string, Balance: real, Type: string, Ssn: string, Branch - no: string, Code: string)
➲Loan (Loan - no: string, Type: string, Amount: real, Ssn: string, Branch - no: string, Code: string
➲Loan (Loan - no: string, Type: string, Amount: real, Ssn: string, Branch - no: string, Code: string

